$$
% Typography and symbols
\newcommand{\msf}[1]{\mathsf{#1}}
\newcommand{\ctx}{\Gamma}
\newcommand{\qamp}{&\quad}
\newcommand{\qqamp}{&&\quad}
\newcommand{\Coloneqq}{::=}
\newcommand{\proves}{\vdash}
\newcommand{\star}[1]{#1^{*}}
\newcommand{\eps}{\varepsilon}
\newcommand{\nul}{\varnothing}
\newcommand{\brc}[1]{\{{#1}\}}
\newcommand{\binopm}[2]{#1~\bar{\oplus}~#2}
\newcommand{\mag}[1]{|{#1}|}
\newcommand{\aequiv}{\equiv_\alpha}
\newcommand{\semi}[2]{{#1};~{#2}}
% Untyped lambda calculus
\newcommand{\fun}[2]{\lambda ~ {#1} ~ . ~ {#2}}
\newcommand{\app}[2]{#1 ~ #2}
\newcommand{\fix}[3]{\msf{fix}~({#1} : {#2}) ~ . ~ #3 }
\newcommand{\truet}{\msf{true}}
\newcommand{\falset}{\msf{false}}
\newcommand{\define}[2]{{#1} \triangleq {#2}}
% Typed lambda calculus - expressions
\newcommand{\funt}[3]{\lambda ~ \left(#1 : #2\right) ~ . ~ #3}
\newcommand{\lett}[4]{\msf{let} ~ \hasType{#1}{#2} = #3 ~ \msf{in} ~ #4}
\newcommand{\letrec}[4]{\msf{letrec} ~ \hasType{#1}{#2} = #3 ~ \msf{in} ~ #4}a
\newcommand{\ift}[3]{\msf{if} ~ {#1} ~ \msf{then} ~ {#2} ~ \msf{else} ~ {#3}}
\newcommand{\rec}[5]{\msf{rec}(#1; ~ #2.#3.#4)(#5)}
\newcommand{\case}[5]{\msf{case} ~ {#1} ~ \{ L(#2) \to #3 \mid R(#4) \to #5 \}}
\newcommand{\pair}[2]{\left({#1},~{#2}\right)}
\newcommand{\proj}[2]{#1 . #2}
\newcommand{\inj}[3]{\msf{inj} ~ #1 = #2 ~ \msf{as} ~ #3}
\newcommand{\letv}[3]{\msf{let} ~ {#1} = {#2} ~ \msf{in} ~ {#3}}
\newcommand{\fold}[2]{\msf{fold}~{#1}~\msf{as}~{#2}}
\newcommand{\unfold}[1]{\msf{unfold}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\poly}[2]{\Lambda~{#1}~.~ #2}
\newcommand{\polyapp}[2]{{#1}~\left[{#2}\right]}
\newcommand{\export}[3]{\msf{export}~ #1 ~\msf{without}~{#2}~\msf{as}~ #3}
\newcommand{\import}[4]{\msf{import} ~ ({#1}, {#2}) = {#3} ~ \msf{in} ~ #4}
% Typed lambda calculus - types
\newcommand{\tnum}{\msf{num}}
\newcommand{\tstr}{\msf{string}}
\newcommand{\tint}{\msf{int}}
\newcommand{\tbool}{\msf{bool}}
\newcommand{\tfun}[2]{#1 \rightarrow #2}
\newcommand{\tprod}[2]{#1 \times #2}
\newcommand{\tsum}[2]{#1 + #2}
\newcommand{\trec}[2]{\mu~{#1}~.~{#2}}
\newcommand{\tvoid}{\msf{void}}
\newcommand{\tunit}{\msf{unit}}
\newcommand{\tpoly}[2]{\forall~{#1}~.~{#2}}
\newcommand{\tmod}[2]{\exists ~ {#1} ~ . ~ #2}
% WebAssembly
\newcommand{\wconst}[1]{\msf{i32.const}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wbinop}[1]{\msf{i32}.{#1}}
\newcommand{\wgetlocal}[1]{\msf{get\_local}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wsetlocal}[1]{\msf{set\_local}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wgetglobal}[1]{\msf{get\_global}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wsetglobal}[1]{\msf{set\_global}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wload}{\msf{i32.load}}
\newcommand{\wstore}{\msf{i32.store}}
\newcommand{\wsize}{\msf{memory.size}}
\newcommand{\wgrow}{\msf{memory.grow}}
\newcommand{\wunreachable}{\msf{unreachable}}
\newcommand{\wblock}[1]{\msf{block}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wloop}[1]{\msf{loop}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wbr}[1]{\msf{br}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wbrif}[1]{\msf{br\_if}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wreturn}{\msf{return}}
\newcommand{\wcall}[1]{\msf{call}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wlabel}[2]{\msf{label}~\{#1\}~{#2}}
\newcommand{\wframe}[2]{\msf{frame}~({#1}, {#2})}
\newcommand{\wtrapping}{\msf{trapping}}
\newcommand{\wbreaking}[1]{\msf{breaking}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wreturning}[1]{\msf{returning}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wconfig}[5]{\{\msf{module}{:}~{#1};~\msf{mem}{:}~{#2};~\msf{locals}{:}~{#3};~\msf{stack}{:}~{#4};~\msf{instrs}{:}~{#5}\}}
\newcommand{\wfunc}[4]{\{\msf{params}{:}~{#1};~\msf{locals}{:}~{#2};~\msf{return}~{#3};~\msf{body}{:}~{#4}\}}
\newcommand{\wmodule}[1]{\{\msf{funcs}{:}~{#1}\}}
\newcommand{\wcg}{\msf{globals}}
\newcommand{\wcf}{\msf{funcs}}
\newcommand{\wci}{\msf{instrs}}
\newcommand{\wcs}{\msf{stack}}
\newcommand{\wcl}{\msf{locals}}
\newcommand{\wclab}{\msf{labels}}
\newcommand{\wcm}{\msf{mem}}
\newcommand{\wcmod}{\msf{module}}
\newcommand{\wsteps}[2]{\steps{\brc{#1}}{\brc{#2}}}
\newcommand{\with}{\underline{\msf{with}}}
\newcommand{\wvalid}[2]{{#1} \vdash {#2}~\msf{valid}}
\newcommand{\wif}[2]{\msf{if}~{#1}~{\msf{else}}~{#2}}
\newcommand{\wfor}[4]{\msf{for}~(\msf{init}~{#1})~(\msf{cond}~{#2})~(\msf{post}~{#3})~{#4}}
% assign4.3 custom
\newcommand{\wtry}[2]{\msf{try}~{#1}~\msf{catch}~{#2}}
\newcommand{\wraise}{\msf{raise}}
\newcommand{\wraising}[1]{\msf{raising}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wconst}[1]{\msf{i32.const}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wbinop}[1]{\msf{i32}.{#1}}
\newcommand{\wgetlocal}[1]{\msf{get\_local}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wsetlocal}[1]{\msf{set\_local}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wgetglobal}[1]{\msf{get\_global}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wsetglobal}[1]{\msf{set\_global}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wload}{\msf{i32.load}}
\newcommand{\wstore}{\msf{i32.store}}
\newcommand{\wsize}{\msf{memory.size}}
\newcommand{\wgrow}{\msf{memory.grow}}
\newcommand{\wunreachable}{\msf{unreachable}}
\newcommand{\wblock}[1]{\msf{block}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wloop}[1]{\msf{loop}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wbr}[1]{\msf{br}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wbrif}[1]{\msf{br\_if}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wreturn}{\msf{return}}
\newcommand{\wcall}[1]{\msf{call}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wlabel}[2]{\msf{label}~\{#1\}~{#2}}
\newcommand{\wframe}[2]{\msf{frame}~({#1}, {#2})}
\newcommand{\wtrapping}{\msf{trapping}}
\newcommand{\wbreaking}[1]{\msf{breaking}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wreturning}[1]{\msf{returning}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wconfig}[5]{\{\msf{module}{:}~{#1};~\msf{mem}{:}~{#2};~\msf{locals}{:}~{#3};~\msf{stack}{:}~{#4};~\msf{instrs}{:}~{#5}\}}
\newcommand{\wfunc}[4]{\{\msf{params}{:}~{#1};~\msf{locals}{:}~{#2};~\msf{return}~{#3};~\msf{body}{:}~{#4}\}}
\newcommand{\wmodule}[1]{\{\msf{funcs}{:}~{#1}\}}
\newcommand{\wcg}{\msf{globals}}
\newcommand{\wcf}{\msf{funcs}}
\newcommand{\wci}{\msf{instrs}}
\newcommand{\wcs}{\msf{stack}}
\newcommand{\wcl}{\msf{locals}}
\newcommand{\wcm}{\msf{mem}}
\newcommand{\wcmod}{\msf{module}}
\newcommand{\wsteps}[2]{\steps{\brc{#1}}{\brc{#2}}}
\newcommand{\with}{\underline{\msf{with}}}
\newcommand{\wvalid}[2]{{#1} \vdash {#2}~\msf{valid}}
% assign4.3 custom
\newcommand{\wtry}[2]{\msf{try}~{#1}~\msf{catch}~{#2}}
\newcommand{\wraise}{\msf{raise}}
\newcommand{\wraising}[1]{\msf{raising}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\wif}[2]{\msf{if}~{#1}~{\msf{else}}~{#2}}
\newcommand{\wfor}[4]{\msf{for}~(\msf{init}~{#1})~(\msf{cond}~{#2})~(\msf{post}~{#3})~{#4}}
\newcommand{\windirect}[1]{\msf{call\_indirect}~{#1}}
% session types
\newcommand{\ssend}[2]{\msf{send}~{#1};~{#2}}
\newcommand{\srecv}[2]{\msf{recv}~{#1};~{#2}}
\newcommand{\soffer}[4]{\msf{offer}~\{{#1}\colon({#2})\mid{#3}\colon({#4})\}}
\newcommand{\schoose}[4]{\msf{choose}~\{{#1}\colon({#2})\mid{#3}\colon({#4})\}}
\newcommand{\srec}[1]{\msf{label};~{#1}}
\newcommand{\sgoto}[1]{\msf{goto}~{#1}}
\newcommand{\dual}[1]{\overline{#1}}
% Inference rules
\newcommand{\inferrule}[3][]{\cfrac{#2}{#3}\;{#1}}
\newcommand{\ir}[3]{\inferrule[\text{(#1)}]{#2}{#3}}
\newcommand{\s}{\hspace{1em}}
\newcommand{\nl}{\\[2em]}
\newcommand{\evalto}{\boldsymbol{\overset{*}{\mapsto}}}
\newcommand{\steps}[2]{#1 \boldsymbol{\mapsto} #2}
\newcommand{\evals}[2]{#1 \evalto #2}
\newcommand{\subst}[3]{[#1 \rightarrow #2] ~ #3}
\newcommand{\dynJ}[2]{#1 \proves #2}
\newcommand{\dynJC}[1]{\dynJ{\ctx}{#1}}
\newcommand{\typeJ}[3]{#1 \proves \hasType{#2}{#3}}
\newcommand{\typeJC}[2]{\typeJ{\ctx}{#1}{#2}}
\newcommand{\hasType}[2]{#1 : #2}
\newcommand{\val}[1]{#1~\msf{val}}
\newcommand{\num}[1]{\msf{Int}(#1)}
\newcommand{\err}[1]{#1~\msf{err}}
\newcommand{\trans}[2]{#1 \leadsto #2}
\newcommand{\size}[1]{\left|#1\right|}
$$
The Inanity of Programming Language Benchmarks
Will Crichton
—
September 18, 2018
Programming language performance benchmarks track the maximum performance of a program, when really we also care about how long it takes to get there.
Software is rarely static. Over time, requirements change, designs improve, features come and go, and the program must gradually evolve as the world changes around it. A fundamental utility of a programming language is to provide tools that improve productivity when evolving software. From a correctness standpoint, this is a major use of static typing—refactors become way less scary when the compiler will let you know if you accidentally typo’d a variable name, or passed a bad parameter to a function, and so on.
To evaluate the utility of a programming language, then, it makes sense to think not in terms of absolutes, but deltas. For scripting languages, this doesn’t make a difference since scripts usually start from zero anyway. That’s why library support and fast iteration times are important for productivity in scripts. For systems languages, the delta is more often against an existing system than starting from scratch.
However, programming language benchmarks take a static view of the world. They say, given a target application, what is the fastest possible implementation of it in a programming language? Benchmarks are often debated on the axis of complexity: is the example too toy to mean anything, or indicative of real workloads? Instead, I want to contest the utility of benchmarks on the axis of time: performance benchmarks should measure how long it takes to improve the performance of a program, not just the program’s maximum performance.
Now, that sounds a bit crazy—how can we possibly test that in a controlled way? And why would we have benchmarks that involve humans, I thought the point was to get rid of those? Yes, there are a lot of problems, and in general human-centric studies of programming language use still have a long way to go. But I want to share a cool example from a paper in my group at Stanford.
Halide is a programming language for efficient image and tensor processing. It’s a neat research project (now a production language!) that defines a DSL for specifying computations on tensors, and then mapping those computations to hardware through “schedules.” An example from their homepage:
Func blur_3x3(Func input) {
Func blur_x, blur_y;
Var x, y, xi, yi;
// The algorithm - no storage or order
blur_x(x, y) = (input(x-1, y) + input(x, y) + input(x+1, y))/3;
blur_y(x, y) = (blur_x(x, y-1) + blur_x(x, y) + blur_x(x, y+1))/3;
// The schedule - defines order, locality; implies storage
blur_y.tile(x, y, xi, yi, 256, 32)
.vectorize(xi, 8).parallel(y);
blur_x.compute_at(blur_y, x).vectorize(x, 8);
return blur_y;
}
It turned out that writing schedules is hard, so my colleague Ravi set out to write an auto-scheduler, culminating in Automatically Scheduling Halide Image Processing Pipelines (SIGGRAPH 2017). To evaluate whether his automatic scheduling algorithm was any good, he ran a study to compare it against the hand-crafted schedules of expert Halide users. Importantly, he measured not just the max speed of their best schedule, but how long it took them to get there. As you can see in the figure, he showed that the two expert programmers took hours to get close to the performance that he could get instantly.
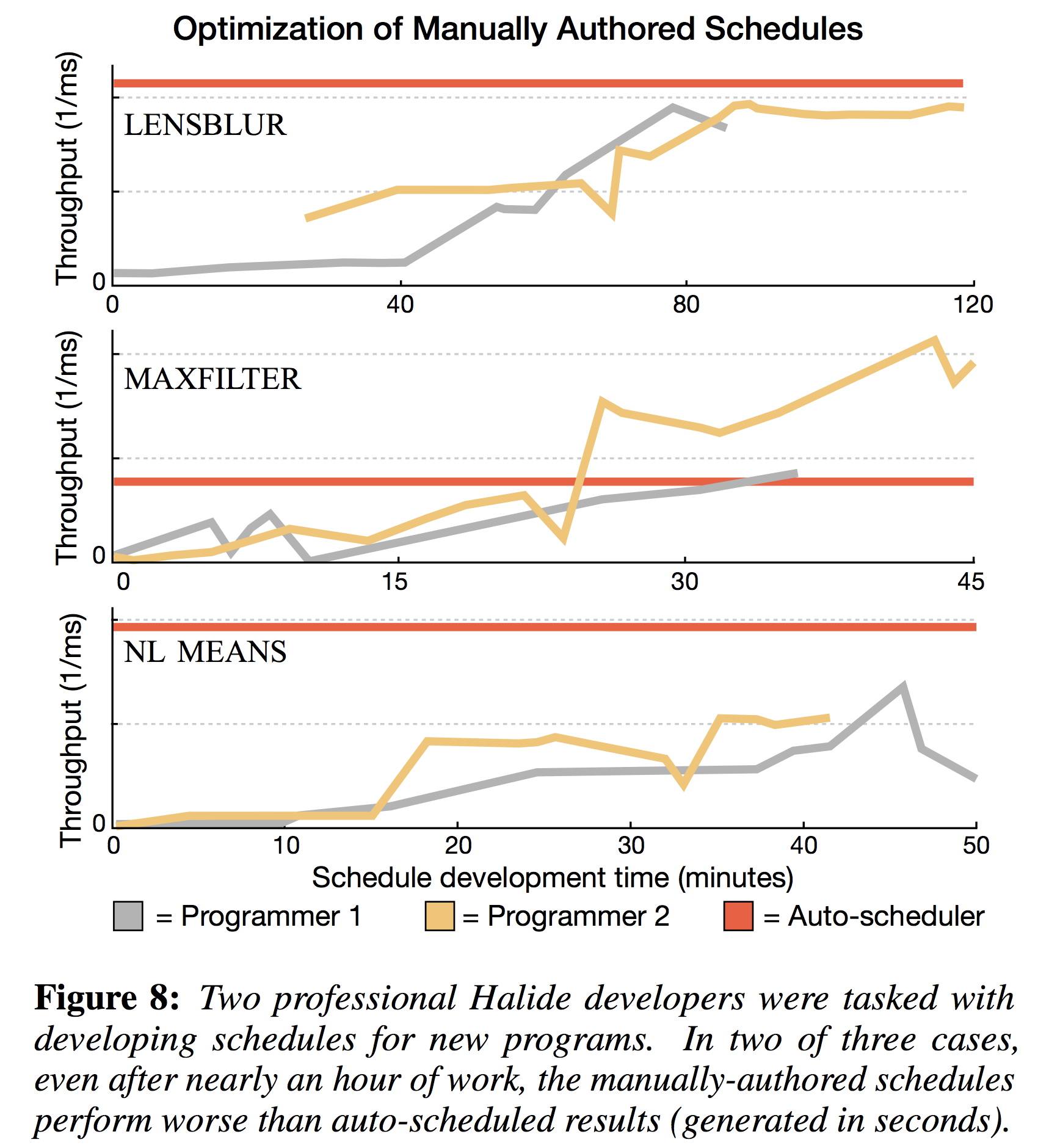
The moral of the story is that I think this kind of combined benchmark/user-study could tell us a lot more about the utility of programming languages than just highly-optimized benchmarks. On one hand, I suspect that it probably takes a decent amount of effort to make a program written in a low-level language that much faster than a high-level one with an optimized runtime. On the other hand, when performance really matters, it will probably take less time to maximize the performance of a low-level program with strict control of the hardware than a high-level program at the mercy of a JIT.
